
This is a sentence in the present perfect tense.
We know it is in the present perfect tense because it has the auxiliary verb HAVE (or HAS) followed by a PAST PARTICIPLE.
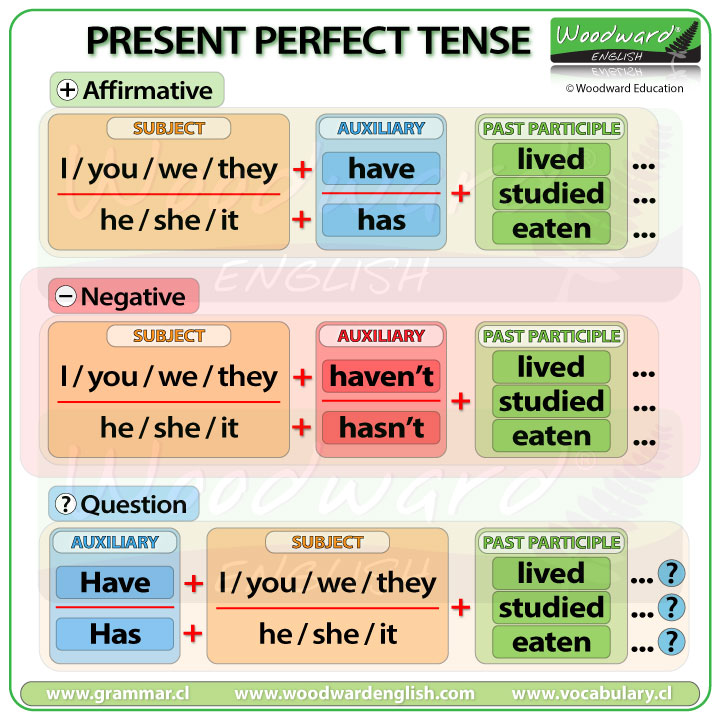
Look at the structure for affirmative sentences in the present perfect tense. The word order is:
subject + have / has + past participle
The past participle can be regular or irregular.
Let’s look at the present perfect tense with regular past participles.
Regular past participles end in ED.
Some example sentences:
Notice how the past participle of these regular verbs is the same as the past simple tense form.
But some past participles are IRREGULAR. For example:
Notice how the past participle of these irregular verbs is different from their past tense form.
I recommend our lesson about 101 Irregular Past Participles with example sentences in English.

In spoken English, we almost always use contractions with the present perfect tense. We contract the subject and the auxiliary have / has.
For example: I have
We contract the subject I with the auxiliary HAVE which becomes I’VE … and then you can add the past participle.
Here is the list of present perfect tense contractions:
Let’s look at some example sentences.
Can you change these present perfect sentences to contain a contraction?
Here are the answers:

Now, let’s look at how to make negative sentences in the present perfect tense.
Look at this affirmative sentence:
There is the auxiliary HAVE and the past participle FINISHED.
How can we make this negative?
To create a negative sentence in the present perfect tense, we just add NOT between the auxiliary HAVE or HAS and the past participle.
However, it is much more common to use a contraction in negative sentences.
You will normally hear:
Look at this affirmative sentence:
How can we make this negative?
To create a negative sentence in the present perfect tense, we just add NOT between the auxiliary HAVE or HAS and the past participle.
However, it is much more common to use a contraction in negative sentences.
You will normally hear:
Let’s look at some more examples of negative sentences in the present perfect tense:
Here is the summary chart to make negatives sentences in the present perfect tense.
We have the subject + negative auxiliary (haven’t/hasn’t) + past participle

Look at this affirmative sentence:
It has the subject THEY, the auxiliary HAVE and the past participle STUDIED.
How can we change this into a question?
To make a question in the present perfect tense, we change the order of the subject with HAVE / HAS.
Look at this affirmative sentence:
How can we make this a question? We change the order of the subject and the auxiliary. The question becomes…
Let’s look at some more examples of present perfect questions:

We can also give short answers to present perfect tense questions.
Look at these questions:
Obviously, you can reply with just YES or NO, but in reality, we almost always give a short answer.
Present perfect short answers use HAVE or HAVEN’T in them.
Let’s look at the first question:
Since this question is HAVE YOU…?
The short answers would be: Yes, I have. … or … No I haven’t.
What would the short answers be for the next two questions?
We can also use question words (what, where, why, etc.) at the beginning of the question. For example:
I hope you found this lesson about the present perfect tense useful.
If you did, please let other people know about it.